ISO 27001: Understanding the Standard
What is ISO 27001?
ISO 27001 is an internationally recognized standard for establishing, implementing, maintaining, and continually improving an information security management system (ISMS).
Elements of the Standard
The ISO 27001 standard is comprised of 11 clauses (0 to 10) and includes a catalogue of 93 proposed controls within its Annex A. Clauses 0-3 introduce the ISO 27001 standard by specifying the scope, normative references, and terms and definitions. Clauses 4-10 make up the core of the ISO 27001 standard. These mandatory clauses establish the management system necessary to implement and maintain effective information security.
Clause 4 – Context of the Organization
Requires that the organization evaluates and accounts for all internal and external issues that may be relevant to its business purpose and could affect the implementation of an ISMS.
Clause 5 – Leadership
Requires that the organization’s top management demonstrate leadership and commitment to the establishment, implementation, maintenance, and improvement of the ISMS.
Clause 6 – Planning
Requires that the organization take actions to address risks and clarify the information security objectives.
Clause 7 – Support
Requires the organization to determine and provide the necessary resources to ensure an adequate level of information security competence and awareness.
Clause 8 – Operation
Requires the organization to plan, implement, and control the processes to meet the information security requirements and to implement the actions determined by the risk treatment plan.
Clause 9 – Performance Evaluation
Requires the organization to monitor, measure, analyze, and evaluate the ISMS to ensure its effective performance. This clause requires an internal audit and management review of the ISMS.
Clause 10 – Improvement
Requires the organization to develop a process to continually improve the suitability, adequacy, and effectiveness of the ISMS.
Annex A
Annex A is a catalogue of 93 security controls, divided over four chapters: Organizational, People, Physical, and Technological. Organizations are not required to implement all Annex A controls. An organization may choose to implement custom controls or controls from a different control set (for example, NIST, PCI DSS, ISO 27701, etc.). Selection of Annex A controls, indicated in the Statement of Applicability (discussed in the Implementation section) depends on the organization’s risk assessment, risk treatment, and specific needs. Look to ISO 27002 for further detail on the Annex A controls, as well as implementation guidance.
What is an ISMS?
An ISMS is a collection of documented policies, processes, procedures, and supporting records for systematically managing an organization’s information security. The ISMS preserves the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information by applying a risk management process and gives confidence to interested parties that risks are adequately managed. An ISMS addresses information security from a holistic perspective. It provides an assessment of risks, a treatment plan to mitigate risks, a plan of action in case a security breach occurs, and assignment of responsibilities to competent individuals. An integrated ISMS enables organization personnel to readily understand information security risks and embrace controls as part of their daily workplace practices.
Objectives of an ISMS
Identify risks faced by the information assets
Provide safeguards to protect the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of assets
Document the information security processes
Assign responsibilities to relevant roles
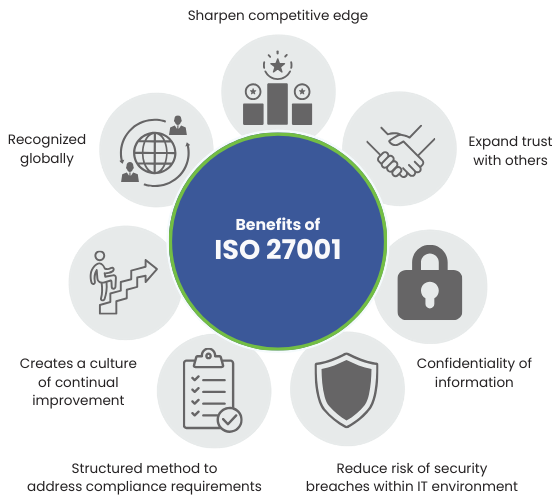
Benefits of ISO 27001
The ISO 27001 Process
1. Appoint an ISO 27001 team
The organization should assemble a team responsible for the ISMS implementation to drive the project and keep it on course.
2. Plan the ISMS
The scope of the ISMS shall be defined and documented. The organization’s information security objectives should be established. A thorough and accurate inventory of all assets within the scope is to be created.
3. Plan and conduct a risk assessment
The organization shall outline its risk assessment methodology then execute the plan. The resulting risk assessment report is a central component of an organization’s ISMS.
4. Write the Statement of Applicability
The Statement of Applicability is the main link between risk assessment and risk treatment in an organization. The Statement of Applicability details the organization’s applicable controls. The document justifies the organization’s choice of including or excluding Annex A controls.
5. Implement a risk treatment plan
Create and implement a risk treatment plan to control the risks identified during the risk assessment. An action plan should be implemented to address risks requiring modification.
6. Build and operate the ISMS
Document and implement all policies, processes, and procedures. The organization shall monitor its ISMS for maintenance and continual improvement.
Internal Audit
Clause 9 of the ISO 27001 standard requires that the organization conduct internal audits of its ISMS to ensure that it is adequately implemented and related control activities are operating effectively. Internal audits must take place at least annually. Internal audit activities must be performed by objective auditors who are independent of the organization’s management.
Dansa D’Arata Soucia (“DDS”) has developed an internal audit program which includes the testing of the ISMS to meet Clauses 4-10, the applicable Annex A controls identified within the Statement of Applicability, and any custom controls.
Certification Audit
The initial certification audit is conducted in two stages. Stage 1 consists of a document review to verify the organization has the required documentation for an operational ISMS. There is a corrective action period between the two stages to allow for the organization to take any corrective actions arising from the Stage 1 audit. Stage 2 is an evidential audit to verify the organization’s ISMS was properly established and implemented and is functioning appropriately. An ISO 27001 certification is valid for 3 years.
Surveillance Audit
Now that you have your certification, you must work to maintain your ISMS. ISO requires a surveillance audit to take place annually during the two calendar years following certification. Each surveillance audit helps the organization get ready for its recertification audit, which takes place at the end of each 3-year cycle. The surveillance audit focuses on key ISMS processes such as management review, corrective action, internal audit, and the implementation of recommendations provided by the organization’s internal auditors.
Looking to take the next step?
For organizations seeking to implement an ISMS in hopes of becoming ISO 27001 certified, DDS can help!
Clause 9 of the ISO 27001 standard requires an organization to have an internal audit of its ISMS performed at least annually. The standard requires the organization to select auditors and conduct audits that ensure objectivity and impartiality of the audit process, meaning it should not be performed by someone internal to the organization who is involved in designing, implementing, and maintaining the ISMS. This is difficult for most small to medium sized organizations that do not have a distinct internal audit department. DDS can cost-effectively perform the internal audit function to prepare your organization for your ISO 27001 certification audit and to meet the annual internal audit
requirements described in Clause 9.
During the internal audit DDS focuses on evaluating your organization’s current ISMS against the ISO 27001 requirements. Our internal audit process aims to be as minimally invasive as possible, while still achieving a value-add list of recommendations that will satisfy the needs of your certifying auditors. We provide a detailed assessment of your compliance, including any gaps, possible nonconformities, as well as opportunities for improvement. DDS has consulted with various certifying auditors to ensure that our internal audit program and reporting methodology are aligned with expectations and give your organization the intended result.
Reach out to us today to discuss your path to ISO 27001 compliance!

Jessica Leone is a senior information security auditor at Dansa D’Arata Soucia LLP, focused on providing SOC 2 and ISO 27001 services to small to midsize organizations.